
PREDICTIVE ANALYTICS
Introduction
predictive analytics is a powerful approach that harnesses the power of data to forecast future trends and behaviors. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, predictive analytics enables organizations to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities before they arise.
The predictions could be for the near future or the more distant future. Predictive analysis can be conducted manually or using machine-learning algorithms. Either way, historical data is used to make assumptions about the future.
Table of content
- Introduction
- Key Components of Predictive Analytics
- Predictive Analytics Process
- Applications of Predictive Analytics
- Examples of predictive analytics
- Benefits of Predictive Analytics
- Bibliography
- Conclusion
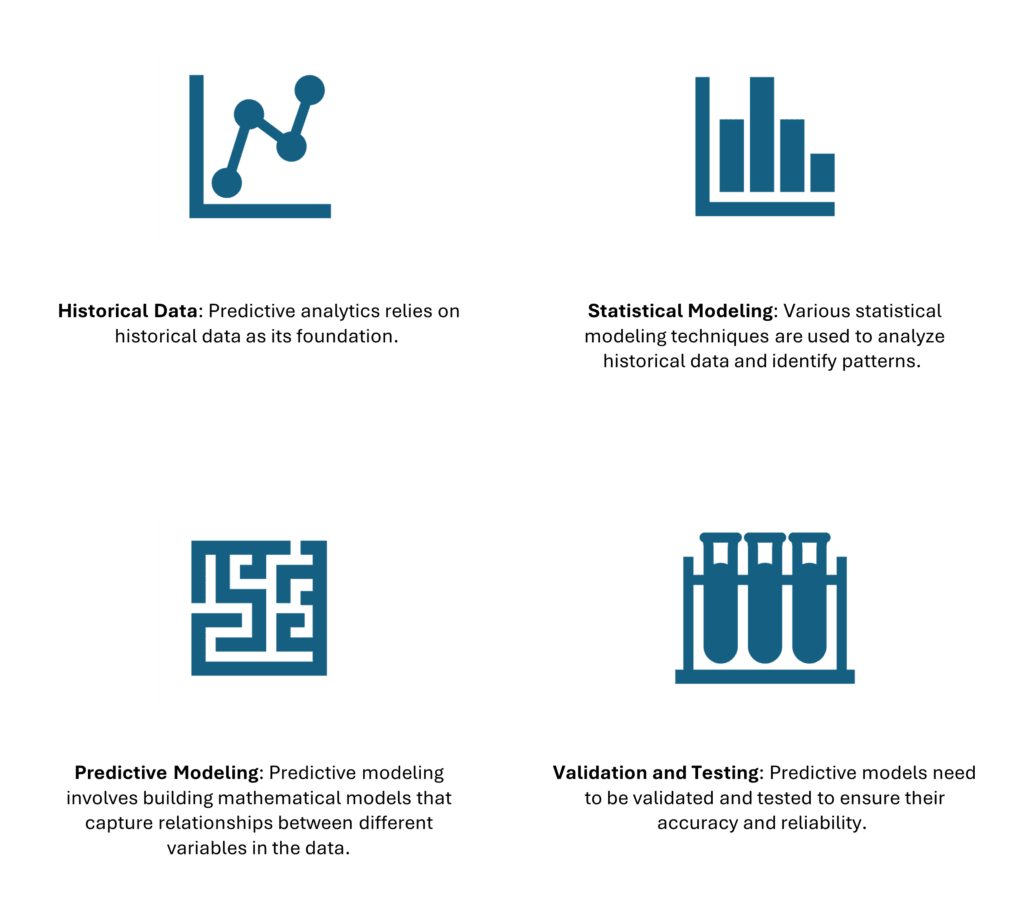
Key Components of Predictive Analytics
- Historical Data: Predictive analytics relies on historical data as its foundation.
- Statistical Modeling: Various statistical modeling techniques are used to analyze historical data and identify patterns.
- Predictive Modeling: Predictive modeling involves building mathematical models that capture relationships between different variables in the data.
- Validation and Testing: Predictive models need to be validated and tested to ensure their accuracy and reliability.
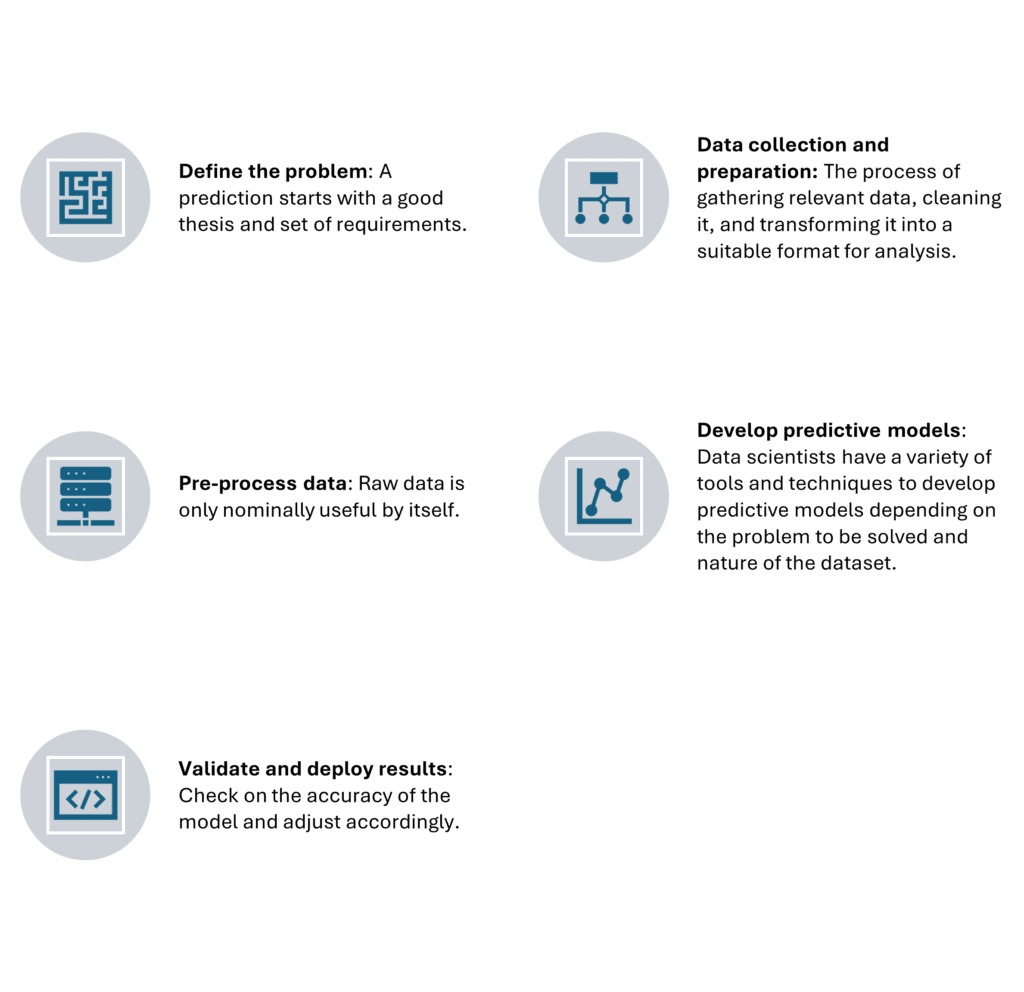
Predictive Analytics Process
- Define the problem: A prediction starts with a good thesis and set of requirements.
- Data collection and preparation: The process of gathering relevant data, cleaning it, and transforming it into a suitable format for analysis.
- Pre-process data: Raw data is only nominally useful by itself.
- Develop predictive models: Data scientists have a variety of tools and techniques to develop predictive models depending on the problem to be solved and the nature of the dataset.
- Validate and deploy results: Check on the accuracy of the model and adjust accordingly.
- Develop predictive models: Data scientists have a variety of tools and techniques to develop predictive models depending on the problem to be solved and the nature of the dataset.
Applications of Predictive Analytics
Finance: Forecasting Future Cash Flow
Every business needs to keep periodic financial records, and predictive analytics can play a big role in forecasting your organization’s future health.
Marketing: Behavioral Targeting
Predictive analytics helps marketers anticipate customer behavior, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize advertising spend.
Manufacturing: Preventing Malfunction
In manufacturing, predictive analytics enables predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, supply chain optimization, and quality control.
Health Care: Early Detection of Allergic Reactions
Predictive analytics aids in patient diagnosis, treatment planning, disease outbreak prediction, and resource allocation in hospitals.
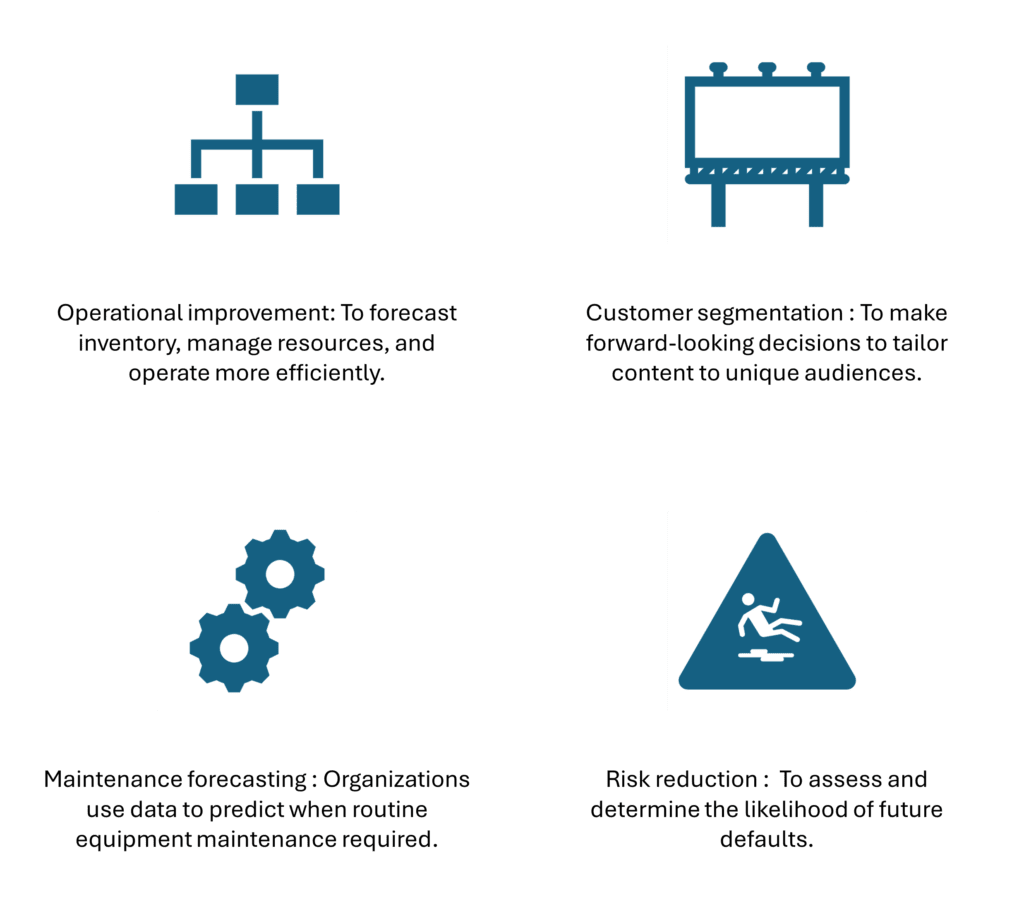
Examples of predictive analytics
- Operational improvement: To forecast inventory, manage resources, and operate more efficiently.
- Customer segmentation: To make forward-looking decisions to tailor content to unique audiences.
- Maintenance forecasting: Organizations use data to predict when routine equipment maintenance is required.
- Risk reduction: To assess and determine the likelihood of future defaults.
Benefits of Predictive Analytics
- Improved Decision-Making
- Enhanced Efficiency
- Competitive Advantage
Bibliography
CONCLUSION
Predictive analytics isn’t just about predicting the future; it’s about shaping it. By harnessing the power of data and advanced analytical techniques, organizations gain invaluable insights that drive strategic decision-making, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge.

